Last Updated on January 26, 2026
When winter’s icy grip threatens to damage your recreational vehicle, proper preparation becomes the difference between a smooth spring startup and costly repairs that could reach thousands of dollars. A comprehensive Winter RV Maintenance Checklist serves as your roadmap to protecting one of your most significant investments while ensuring countless future adventures remain within reach.
The recreational vehicle industry has seen unprecedented growth, with over 11.2 million households owning an RV as of 2026 [1]. Yet many owners underestimate the critical importance of winter preparation, leading to expensive freeze damage, mechanical failures, and shortened vehicle lifespans. Whether storing your RV for the season or planning winter travels, following a systematic maintenance approach protects both your investment and peace of mind.
Key Takeaways
• Winterizing plumbing systems prevents costly freeze damage that can exceed $5,000 in repairs
• Battery maintenance and storage extends battery life by up to 50% when properly executed
• Engine and generator preparation ensures reliable performance and prevents fuel system degradation
• Exterior protection measures shield your RV from harsh weather elements and UV damage
• Professional inspection timing identifies potential issues before they become expensive problems
Understanding Winter RV Challenges

Winter presents unique challenges for recreational vehicles that differ significantly from standard automotive winterization. RVs contain complex systems including fresh water, gray water, and black water tanks, along with extensive plumbing networks that extend throughout the vehicle. These systems become vulnerable when temperatures drop below freezing, potentially causing catastrophic damage.
The thermal dynamics of RVs create additional complications. Unlike homes with consistent insulation and heating, RVs feature thinner walls and multiple potential air leaks. This construction makes them susceptible to rapid temperature changes and uneven heating distribution. Understanding these vulnerabilities helps RV owners prioritize maintenance tasks effectively.
Regional climate considerations also play crucial roles in winter preparation. RVers in mild climates may focus on humidity control and occasional use preparation, while those in harsh winter regions require complete winterization protocols. The maintenance approach must align with specific geographic and usage requirements.
Pre-Winter Assessment and Planning
Timing Your Winter RV Maintenance Checklist
Early preparation proves essential for effective winter RV care. Begin your Winter RV Maintenance Checklist at least 4-6 weeks before anticipated storage or first freeze. This timeline allows adequate time for identifying issues, ordering parts, and scheduling professional services when needed.
Weather monitoring becomes crucial during this preparation phase. Track local weather forecasts and historical freeze dates for your area. Many RV owners make the mistake of waiting too long, then rushing through critical maintenance steps when unexpected cold weather arrives.
Maintenance scheduling should coordinate with your RV usage plans. Those planning winter travels require different preparation than seasonal storage. Create a customized timeline that aligns with your specific needs and local climate patterns.
Essential Tools and Supplies
Gathering proper tools and supplies before beginning work streamlines the maintenance process and ensures thorough completion. Basic hand tools including wrenches, screwdrivers, and pliers handle most maintenance tasks. Specialized RV tools such as tank drain wrenches and water heater bypass kits prove essential for plumbing work.
Supply inventory should include RV antifreeze (propylene glycol type), fuel stabilizers, battery maintenance equipment, and various sealants. Quality matters significantly when selecting supplies. Cheap antifreeze or fuel additives may provide inadequate protection, leading to expensive damage.
Safety equipment including gloves, safety glasses, and proper ventilation ensures safe maintenance procedures. Many winterization chemicals require careful handling and adequate ventilation during application.
Exterior Winter RV Maintenance Checklist
Roof and Structural Inspection
Roof integrity represents the first line of defense against winter weather. Begin exterior maintenance by thoroughly inspecting the roof surface for cracks, punctures, or worn sealant areas. Sealant degradation accelerates in cold weather, making pre-winter repair essential.
Structural components including roof vents, air conditioning units, and antenna mounts require careful examination. Look for loose mounting hardware, cracked housings, or damaged gaskets. Preventive repairs cost significantly less than water damage restoration.
Gutter and drainage systems need clearing of debris and inspection for proper water flow. Clogged gutters can cause ice dams and water backup, leading to interior damage. Ensure all drainage paths function correctly before winter weather arrives.
Exterior Sealing and Protection
Comprehensive sealing protects against moisture infiltration during winter months. Inspect and reseal around windows, doors, exterior compartments, and utility connections. High-quality sealants designed for RV applications provide superior protection compared to generic products.
Window and door maintenance includes checking weatherstripping, adjusting hardware, and ensuring proper closure. Lubricate moving parts with appropriate lubricants that remain effective in cold temperatures. Frozen locks or stuck windows create access problems during winter storage checks.
Exterior surface protection may include washing, waxing, or applying protective covers. UV protection remains important even during winter months, particularly in sunny, cold climates where snow reflection intensifies UV exposure.
Tire and Wheel Care
Tire pressure management becomes critical as temperatures drop. Cold weather reduces tire pressure approximately 1-2 PSI per 10-degree temperature decrease. Regular monitoring prevents under-inflation damage and ensures proper weight distribution.
Tire inspection should identify wear patterns, sidewall damage, or embedded objects. Age-related deterioration accelerates in cold weather, making thorough inspection essential. Replace questionable tires before winter storage or travel.
Wheel bearing maintenance includes inspection and lubrication according to manufacturer specifications. Bearing failure during winter travel can strand RVers in dangerous conditions. Professional bearing service may be warranted for older units or high-mileage vehicles.
Interior Systems Winter RV Maintenance Checklist
Plumbing System Winterization
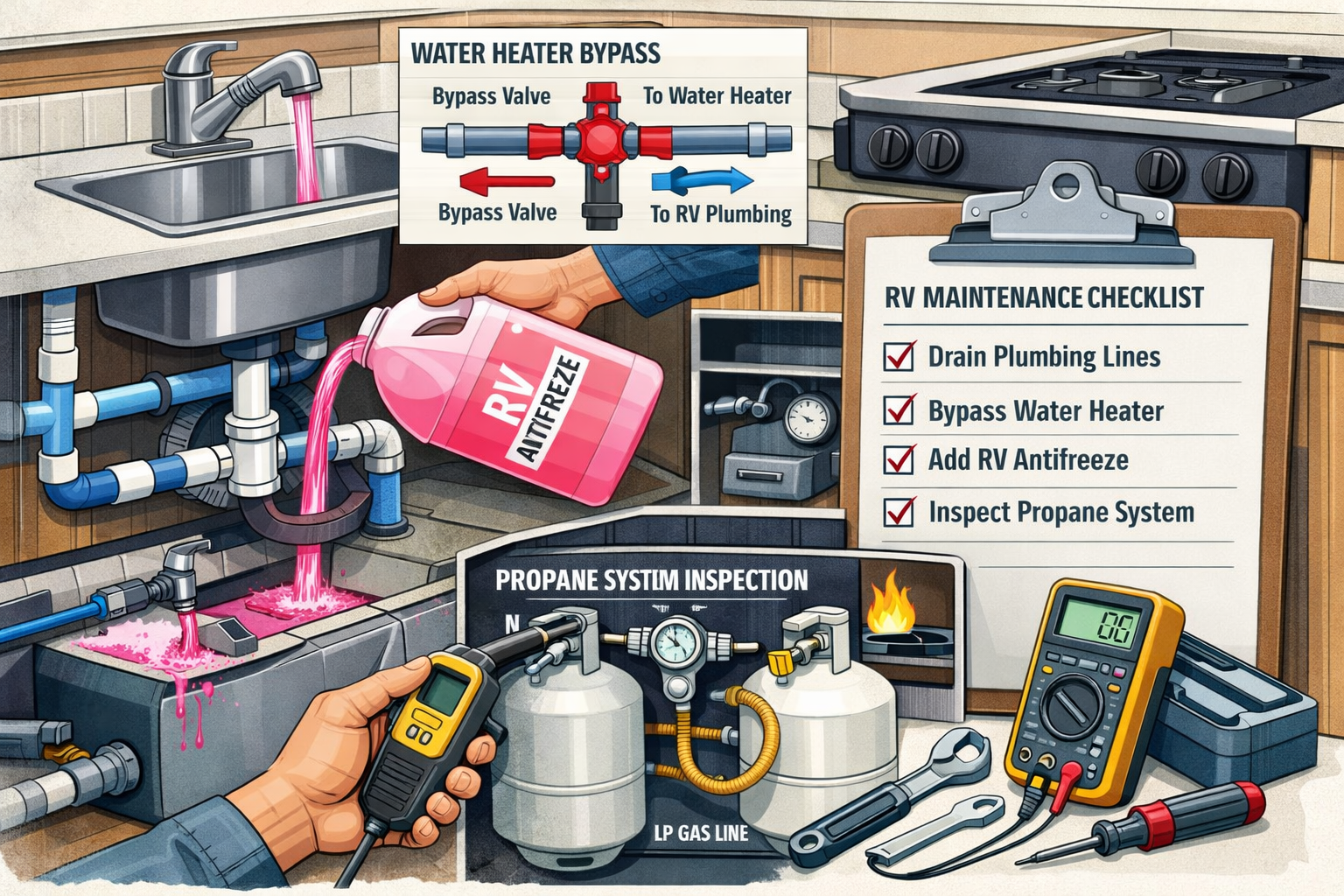
Water system protection represents the most critical aspect of winter RV maintenance. Frozen water lines can burst, causing extensive damage throughout the vehicle. Complete drainage of all water systems provides the foundation for effective winterization.
Systematic draining begins with emptying fresh water, gray water, and black water tanks. Water heater drainage requires specific procedures including pressure relief valve operation and complete tank evacuation. Low point drains remove water from supply lines throughout the vehicle.
Antifreeze application follows complete system drainage. Use only propylene glycol-based RV antifreeze designed for potable water systems. Ethylene glycol automotive antifreeze is toxic and should never be used in RV water systems. Pump antifreeze through all fixtures until pink antifreeze flows from each tap.
Propane System Maintenance
Propane system inspection ensures safe operation during winter months. Visual inspection of lines, connections, and appliances identifies potential leak sources or damage. Professional testing may be required for older systems or when problems are suspected.
Tank maintenance includes checking expiration dates, valve operation, and mounting security. Propane tanks have specific inspection and certification requirements that vary by jurisdiction. Expired tanks require professional recertification before use.
Appliance preparation involves cleaning, inspection, and operational testing of propane-powered equipment. Furnace maintenance includes filter replacement, vent inspection, and operational testing. Water heater service may require professional attention for optimal winter performance.
Electrical System Care
Battery maintenance significantly impacts winter RV reliability. Lead-acid batteries lose capacity in cold weather and require special care during storage. Removal and indoor storage provides optimal protection for conventional batteries.
Charging system inspection includes testing alternator output, checking connections, and verifying proper operation. Solar panel maintenance involves cleaning panels and checking controller operation. Winter sun angles reduce solar charging efficiency, making system optimization important.
12-volt system testing should verify proper operation of lights, pumps, and control systems. Connection cleaning prevents corrosion-related failures during winter storage. Disconnect procedures may be necessary for extended storage periods.
Engine and Mechanical Systems
Engine Winterization
Engine preparation varies significantly between gasoline and diesel powerplants. Gasoline engines require fuel stabilization, oil changes, and cooling system service. Diesel engines need additional considerations including fuel gelling prevention and glow plug system maintenance.
Cooling system service includes antifreeze testing, leak inspection, and hose examination. Proper antifreeze concentration prevents freeze damage while providing corrosion protection. Pressure testing identifies potential leak sources before they cause problems.
Oil change timing should occur before winter storage to remove contamination and provide fresh lubrication. Filter replacement accompanies oil changes for optimal engine protection. Quality lubricants designed for extended storage provide superior protection.
Generator Maintenance
Generator winterization follows similar principles to main engine preparation but requires additional considerations. Load testing verifies proper operation under typical usage conditions. Fuel system preparation includes stabilizer addition and complete fuel system treatment.
Air filter service ensures adequate airflow for proper operation. Spark plug inspection and replacement maintain reliable starting and smooth operation. Exercise schedules during storage prevent fuel system problems and maintain operational readiness.
Sound dampening system maintenance includes inspection of baffles, gaskets, and mounting hardware. Exhaust system inspection identifies potential carbon monoxide hazards or performance issues.
Storage Preparation and Long-term Care
Indoor vs. Outdoor Storage Considerations
Storage location significantly impacts winter maintenance requirements. Indoor storage provides superior protection but may not be available or affordable for all RV owners. Climate-controlled facilities offer optimal protection for high-value units.
Outdoor storage preparation requires additional protective measures including covers, ventilation, and pest control. Ground preparation ensures proper drainage and prevents moisture problems. Security considerations include alarm systems and physical barriers.
Ventilation requirements prevent moisture buildup during storage. Roof vents should remain slightly open to allow air circulation while preventing precipitation entry. Moisture absorbers help control humidity levels inside stored units.
Pest Prevention and Control
Rodent prevention becomes critical during winter storage when small animals seek warm shelter. Entry point sealing includes exhaust outlets, vents, and any openings larger than 1/4 inch. Steel wool provides effective temporary sealing for many openings.
Insect control involves thorough cleaning and elimination of food sources. Ant prevention requires special attention to sweet substances and moisture sources. Professional treatment may be necessary for persistent pest problems.
Monitoring systems help detect pest intrusion during storage. Regular inspections allow early intervention before significant damage occurs. Documentation of pest prevention measures assists with insurance claims if damage occurs.
Climate Control and Ventilation
Humidity control prevents mold, mildew, and condensation damage during storage. Dehumidifiers may be necessary in humid climates or enclosed storage facilities. Moisture monitoring helps maintain optimal conditions.
Temperature management protects sensitive components and materials. Heating systems may be necessary to prevent freeze damage in partially winterized units. Insulation improvements can reduce heating costs and improve protection.
Air circulation prevents stagnant conditions that promote mold growth. Fan operation during storage visits helps maintain air movement. Ventilation planning balances moisture control with energy efficiency.
Professional vs. DIY Maintenance
When to Seek Professional Help
Complex systems may require professional expertise for proper maintenance. Propane system repairs should always involve certified technicians due to safety considerations. Electrical system problems may exceed DIY capabilities and require professional diagnosis.
Warranty considerations may mandate professional service for certain components. Documentation requirements for warranty claims often specify professional maintenance. Cost-benefit analysis should consider potential warranty implications.
Safety concerns should always favor professional service when in doubt. Carbon monoxide risks associated with propane and generator systems require expert attention. Electrical hazards can cause injury or fire if improperly handled.
Cost-Benefit Analysis
Professional service costs vary significantly by region and service complexity. Basic winterization typically costs $200-500 when professionally performed. Complex repairs can quickly exceed DIY capabilities and may require professional intervention regardless of initial approach.
DIY savings can be substantial for routine maintenance tasks. Tool investment should be considered in cost calculations for occasional DIY maintenance. Time requirements may favor professional service for complex procedures.
Risk assessment should consider potential damage costs versus service expenses. Insurance implications may affect coverage for DIY maintenance errors. Professional liability provides protection that DIY approaches cannot match.
Troubleshooting Common Winter Issues
Freeze Damage Prevention and Response
Early detection of freeze damage minimizes repair costs and prevents secondary damage. Warning signs include unusual sounds, visible ice, or system malfunctions. Immediate response can prevent minor problems from becoming major repairs.
Temporary repairs may allow continued use while permanent solutions are arranged. Emergency supplies should include pipe repair clamps, electrical tape, and temporary sealants. Professional consultation helps determine appropriate temporary measures.
Documentation procedures assist with insurance claims and warranty issues. Photographic evidence provides valuable support for damage claims. Repair estimates should be obtained promptly to support insurance processing.
Electrical System Problems
Battery failure represents the most common winter electrical issue. Jump starting procedures should follow manufacturer guidelines to prevent damage. Charging system problems may require professional diagnosis and repair.
Connection corrosion accelerates in winter conditions due to moisture and temperature cycling. Cleaning procedures should use appropriate materials and techniques. Protective coatings help prevent future corrosion problems.
System testing helps identify problems before they cause failures. Multimeter use allows accurate diagnosis of electrical issues. Professional consultation may be necessary for complex electrical problems.
Mechanical System Failures
Engine starting problems often result from battery, fuel, or ignition system issues. Diagnostic procedures should follow systematic approaches to identify root causes. Emergency starting may require jump starting or auxiliary power sources.
Fuel system problems can strand RVers in dangerous winter conditions. Fuel quality issues including water contamination or gelling require specific treatments. Professional service may be necessary for fuel system repairs.
Heating system failures create safety and comfort issues during winter travel. Troubleshooting procedures should prioritize safety over convenience. Alternative heating may be necessary while repairs are completed.
Spring Startup Procedures

De-winterization Process
Systematic de-winterization ensures safe and reliable spring startup. Antifreeze removal requires thorough flushing of all water systems. Sanitization procedures eliminate bacteria and restore potable water quality.
System testing verifies proper operation after winter storage. Leak detection identifies any damage that occurred during storage. Operational testing confirms all systems function correctly before travel.
Documentation review helps track maintenance history and identify upcoming service requirements. Warranty tracking ensures compliance with manufacturer requirements. Service scheduling allows proactive maintenance planning.
System Testing and Inspection
Comprehensive testing covers all major systems and components. Water system pressure testing identifies leaks and verifies proper operation. Electrical system testing confirms battery condition and charging system operation.
Propane system testing should include leak detection and appliance operation verification. Professional testing may be required for safety certification. Operational testing verifies proper appliance function.
Road testing identifies any mechanical issues that developed during storage. Brake testing ensures safe stopping capability. Tire inspection verifies proper pressure and condition after storage.
Conclusion
A comprehensive Winter RV Maintenance Checklist serves as essential protection for recreational vehicle investments while ensuring reliable performance for years to come. The systematic approach outlined in this guide addresses critical systems including plumbing, electrical, mechanical, and structural components that require specific winter preparation.
Proactive maintenance prevents costly repairs and extends RV lifespan significantly. The investment in proper winter preparation typically pays for itself by preventing a single major repair incident. Professional consultation should supplement DIY efforts when safety or complexity concerns arise.
Start your winter preparation early by creating a customized maintenance schedule based on your specific RV type, usage patterns, and storage conditions. Document all maintenance activities to support warranty claims and track system performance over time. Regular maintenance combined with proper winter preparation ensures countless future adventures in your recreational vehicle.
Take action today by downloading manufacturer maintenance schedules, gathering necessary supplies, and beginning your winter preparation process. Your RV investment deserves protection that only comprehensive maintenance can provide.
References
[1] Recreation Vehicle Industry Association. (2026). 2026 RV Shipment and Ownership Statistics. RVIA Market Research Report.





